I Created a Shader Language That Converts to GLSL / WGSL
Made by Claude Code
https://github.com/tseijp/glre
Development Background
WebGPU Emerges as a More Powerful API Than WebGL
The WebGL library Three.js is advancing WebGPU support, and with Apple's support progressing, its practicality is increasing. WebGL is written in GLSL (OpenGL Shading Language), while WebGPU is written in WGSL (WebGPU Shading Language). When using WebGPU with Three.js, you write in their proprietary TSL (Three.js Shading Language).
Compute Shaders Emerge for Non-Rendering GPU Usage Like AI
WebGL shaders were for image and 3DCG rendering, but compute shaders can now be leveraged in browsers through the WebGPU API. I tried implementing particles with Three.js, but compute shaders didn't work properly.
Why I Wanted to Make It
I had long wanted to work with WebGPU, so I started studying it. I had developed a shader rendering library when learning WebGL. I began developing WebGPU support for own library. WGSL for WebGPU implementation has Rust lang like syntax. The WebGPU API requires data transmission from the CPU to the GPU in advance. I wanted automatic configuration from shader code, so I had Claude Code create WebGPU support and intermediate language in about a month.
Desired Features
Three.js Shader Language Compatible Output to Both GLSL and WGSL
WebGPU has compute shaders and storage functionality for saving calculation results as variables. Since compute shaders are new WebGPU technology, I needed to implement equivalent functionality on the WebGL side. To achieve equivalent behavior in WebGL, I automated CPU and GPU processing, such as writing shader calculation results to images. Compute shaders in the developed intermediate language work on both WebGL and WebGPU.
Automatic Error Detection by Claude Code
For vector operations with different lengths like vec3 and vec2, if TypeScript can display errors beforehand, Claude Code can automatically detect them through IDE MCP. If Claude Code automatically detects errors, it can automatically fix them without confirming error messages from browser dev tools.
Automatic Shader Implementation by Claude Code
If TypeScript can output errors, Claude Code can automatically implement that error, so describing the desired image will produce that image. Intermediate language development is also Claude Code's specialty. I simply passed Three.js shading language documentation as requirements and specifications and had it implemented.
Development
SSH from Smartphone to PC and Operate Claude Code via tmux
PC and smartphone are configured to be on the same VPN using Tailscale. PC's development environment runs containers using VSCode's devcontainer. From the smartphone, I use a Termux to execute the following commands. I use tmux to check smartphone operation results on PC later and synchronize output.
ssh ${username}@${address}
docker exec -u node -it ${docker_id} bash
tmux -u new -A -t dev
claude
Output Implementation Plans as Requirements Definition → Comment Technical Specifications
I used prompts like the following. First, I had Claude Code read prepared markdown and files needed for modifications, then output implementation plans as requirements definition. I added technical specifications to the implementation plan before having it implemented.
- **MainTask [1]**
- **SubTask [1.1]**
- Read(`.articles/Q&A_boytchev_tsl-textures_Wiki.md`)
- Read(`.articles/Three.js_Shading_Language.md`)
- Read(`.articles/WebGPU_from_WebGL.md`)
- **SubTask [1.2]**
- Read(`packages/core/src/node/build.ts`)
- Read(`packages/core/src/node/create.ts`)
- Read(`packages/core/src/node/scope.ts`)
- Read(`packages/core/src/node/types.ts`)
- Write(`.articles/2025${M}${D}_issue_${this_issue_title}.md`)
- Interrupt
- **MainTask [2]**
- Fix after confirming Feedback
Implementation Automation
After some development was complete, I had demo code created and passed error messages from running the code along with cause predictions to Claude for correction. Every time errors occurred , I threw them to Claude, had implementation plans output, and humans reviewed and refined technical specifications.
Language Specifications and Features
TypeScript Shader Language to GLSL and WGSL
It supports basic GLSL / WGSL syntax, and since it's TypeScript, you can externalize types and code as modules. I prepared builtin functions and variables common to both GLSL/WGSL, like floor functions and uv variables.
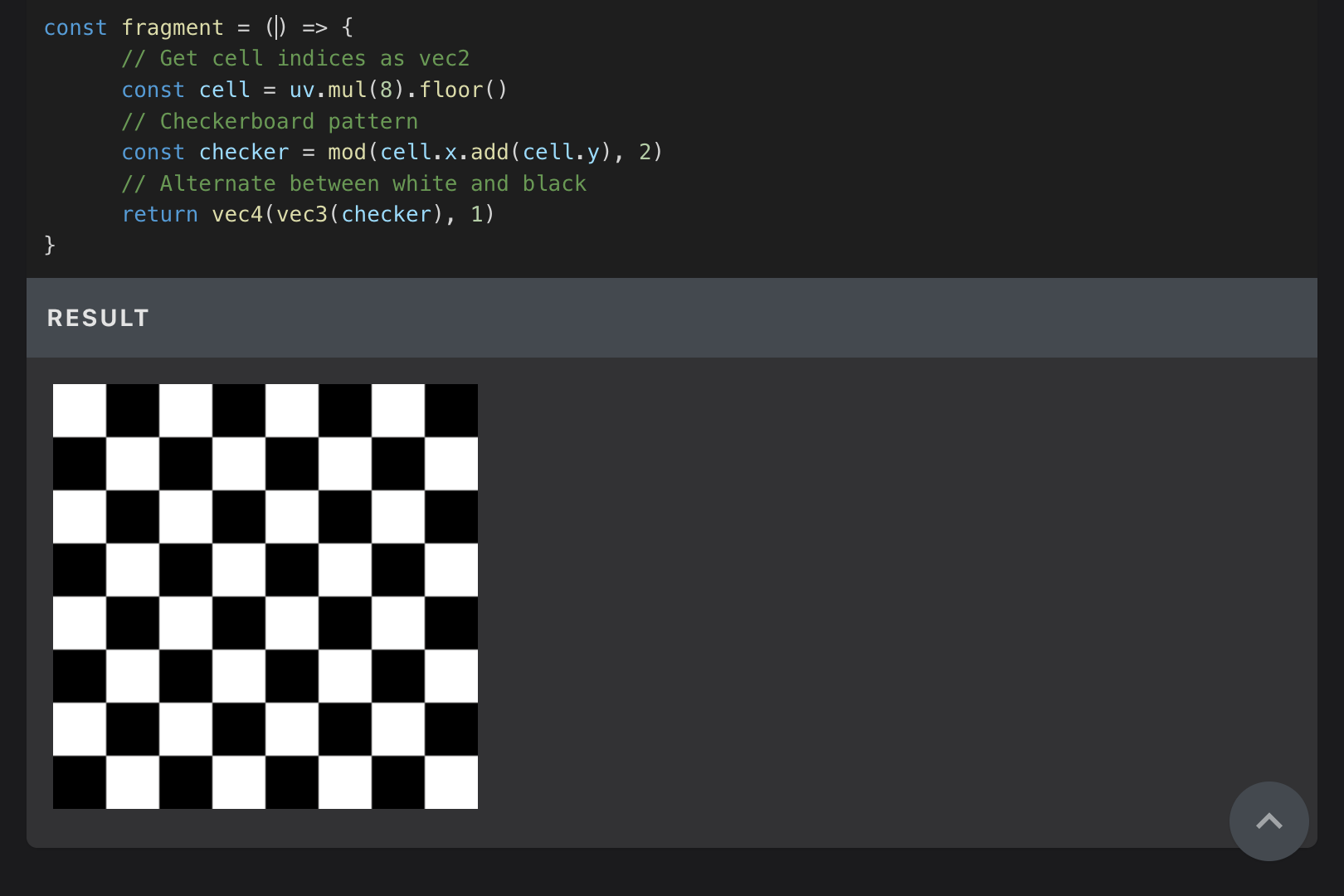
const fragment = () => {
const cell = uv.mul(8).floor()
const checker = mod(cell.x.add(cell.y), 2)
return vec4(vec3(checker), 1)
}
You can configure uniform/varying/attribute for compute/fragment/vertex shaders from the intermediate language. Buffer layout and other CPU-to-GPU data transmission settings are automatically constructed.
As shown below, you can use TypeScript as a macro substitute to output intermediate language.
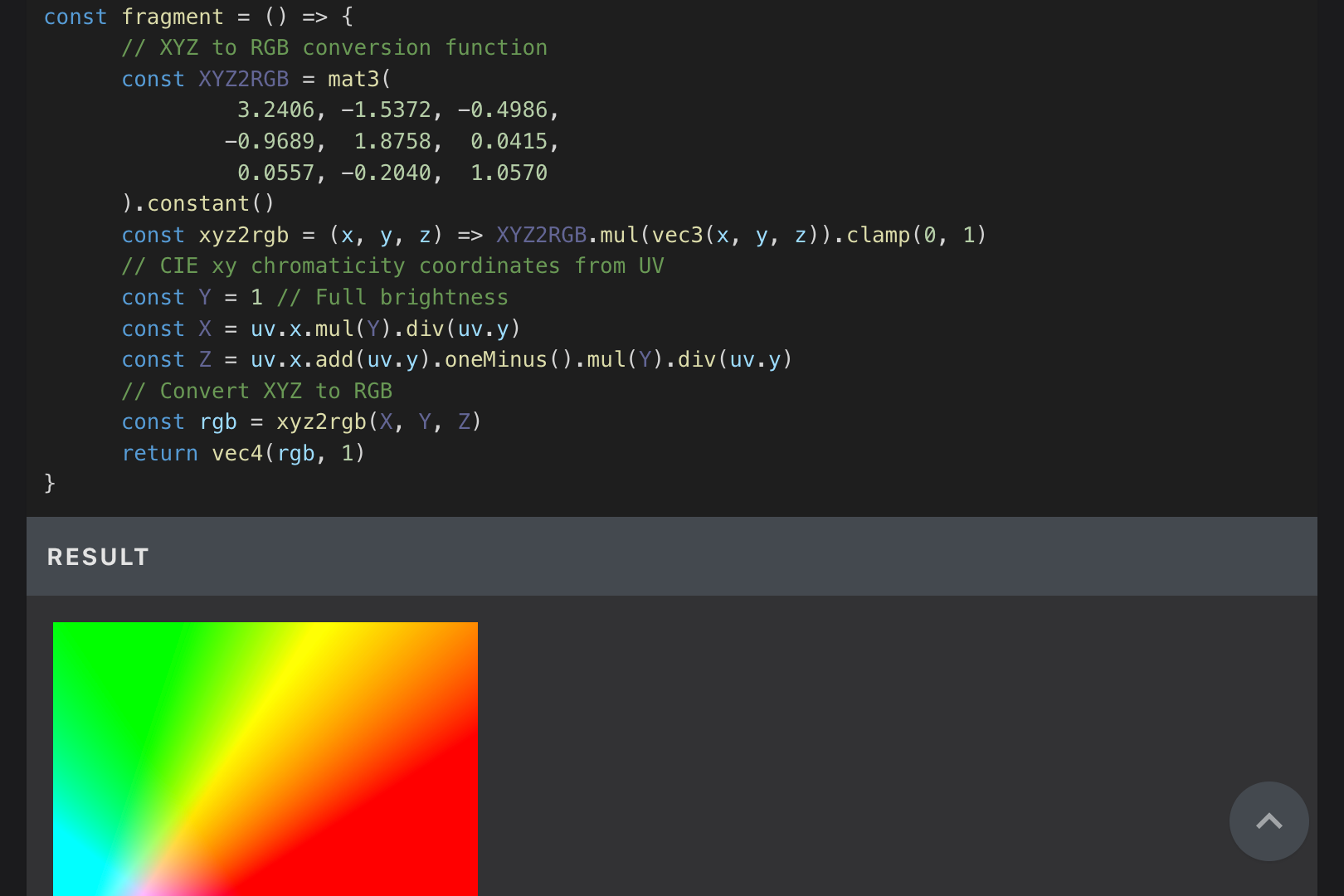
const xyz2rgb = (x, y, z) => XYZ2RGB.mul(vec3(x, y, z)).clamp(0, 1)
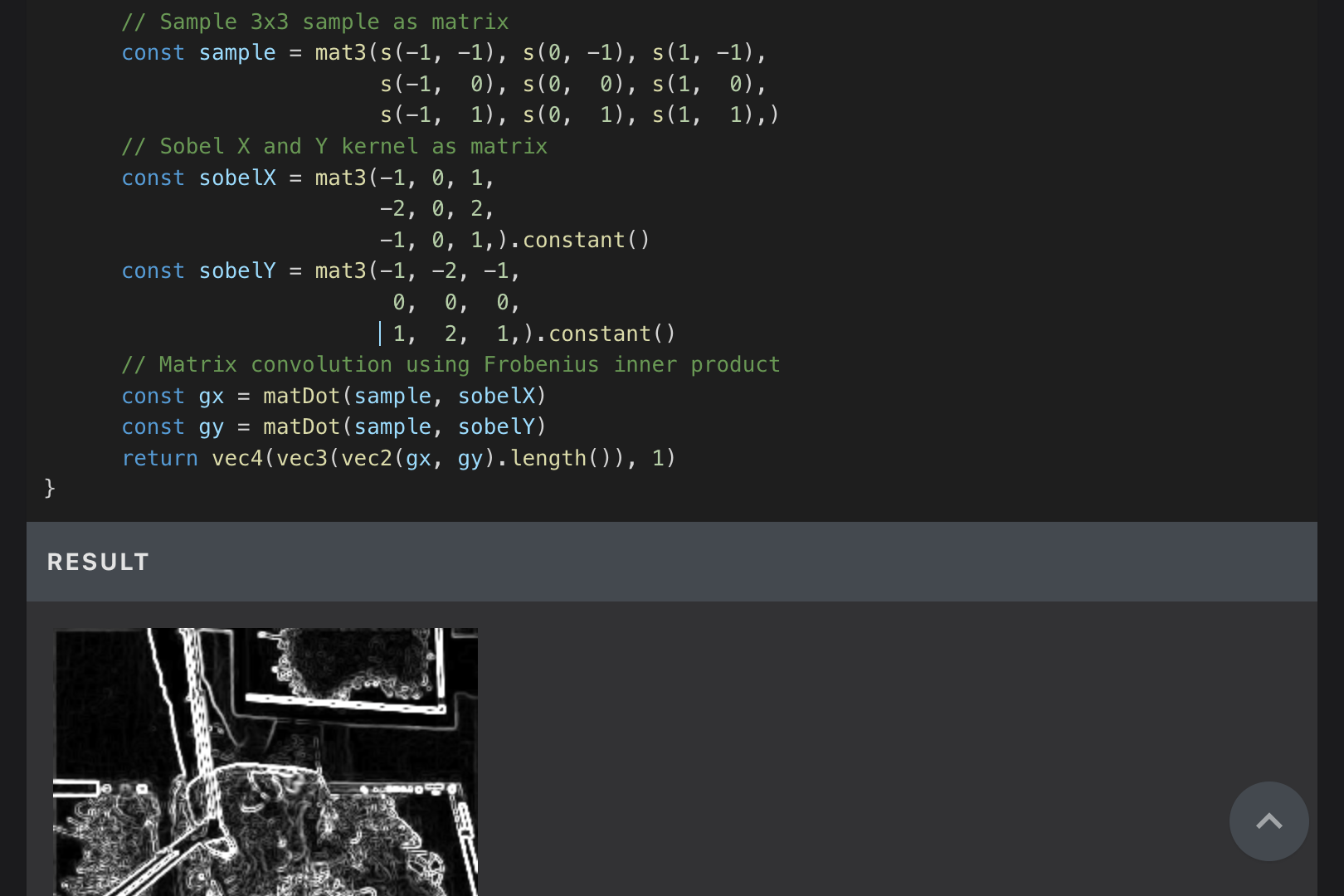
Tutorial Creation
Since I only somewhat understood GLSL and was new to both WGSL and TSL, I had tutorials created for my own study. There are also demos that I couldn't think of myself, like edge detection.
Porting 2024 Paper Raymarch Code
Raymarch is a technique 3D rendering from implicit functions. Raymarch can be computationally heavy, but recent research suggests that mathematical optimization is possible.
Optimization is possible for harmonic functions up to 4 dimensions - it seems like an insanely advanced technique from another dimension, but the implementation is simple, so I asked Claude to implement it. The metallic and roughness seem slightly off from the original code, but it seems to render with lighter processing.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9h13FPuBvM8
Try it myself
Implementing Compute Shaders That Work on Both WebGL and WebGPU
Compute shaders like the following convert to both GLSL and WGSL and can operate on both WebGL/WebGPU.
const compute = Fn(([id]: [Vec3]) => {
const pos = positions.element(id.x).toVar('pos')
const vel = velocities.element(id.x).toVar('vel')
pos.assign(pos.add(vel.mul(0.01)))
If(pos.x.lessThan(0.0).or(pos.x.greaterThan(1.0)), () => {
vel.x.assign(vel.x.mul(-1.0))
pos.x.assign(pos.x.clamp(0.0, 1.0))
})
If(pos.y.lessThan(0.0).or(pos.y.greaterThan(1.0)), () => {
vel.y.assign(vel.y.mul(-1.0))
pos.y.assign(pos.y.clamp(0.0, 1.0))
})
positions.element(id.x).assign(pos)
velocities.element(id.x).assign(vel)
})
Running Same Code compute shader
WebGL does not have compute shaders, so we implemented a similar functionality using texture buffers to store and retrieve data. And since you output the calculation results as fragColor and write to textures, normally you can only use one storage. So I use WebGL2's Multiple Render Targets and reproduce multiple storage.
Future Prospects
Currently, I'm strengthening type safety from created sample code and fixing bugs when they exist. I previously created a playground site where you could upload GLSL. Now that TSL support is complete, I want to make a site where you can write shaders in TypeScript.
Technical Implementation Details
Abstract Syntax Tree Design
I previously created a library called glrb for writing shader-like code in Ruby. However, glrb couldn't output multi-line scopes or define functions. Learning from that experience, I implemented multi-line scopes and function definitions this time to avoid everything being output as one-liners. I referenced materials about abstract syntax trees. I didn't think binary trees were necessary, so while not a complete abstract syntax tree, I constructed something tree-like. Each node in the tree structure is constructed by a create function. It uses exactly the same arguments as React.createElement and saves tree structures using children.
const create = (type, props, ...args) => {
Since constructing abstract syntax trees the same way as React, you can also write shaders in JSX.
<script type="module" src="https://esm.sh/tsx"></script>
<script type="text/babel">
/** @jsx create */
import { create, uv } from 'https://esm.sh/glre@latest'
document.body.innerText = (
<scope>
<declare>
{uv.x}
<variable id="x" />
</declare>
<return>
<conversion>
vec4
<variable id="x" />
{0.4}
{0.6}
{0.8}
</conversion>
</return>
</scope>
)
</script>
The above code outputs as follows:
var x: f32 = (out.position.xy / iResolution).x;
return vec4f(x, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8);
Type Inference System
const fragment = Fn(([uv]: [Vec2]) => {
const x = uv.x.toVar('x')
return vec4(x, 0.4, 0.8, 1)
})
I needed to implement type inference in both JavaScript and TypeScript.
To convert the above fragment function to fn fragment(uv: vec2f) -> vec4f,
I needed JavaScript to infer the types of arguments and return value.
I infer types by checking the tree structure to determine that the uv argument is vec2 and the return value is vec4.
I also implemented TypeScript-side type inference using generics.
To display errors in the IDE,
Separate from type inference for WGSL code output,